Tuyau sans soudure en acier inoxydable
Dureté :
Les tubes en acier inoxydable sont couramment utilisés pour mesurer la dureté Brinell, Rockwell et Vickers.Dureté Brinell Parmi les normes de tuyaux en acier inoxydable, la dureté Brinell est la plus largement utilisée, et la dureté du matériau est souvent exprimée par le diamètre d'indentation, qui est à la fois intuitif et pratique.Cependant, il ne convient pas aux tubes en acier en acier plus dur ou plus fin.
Dureté Rockwell :
Le test de dureté Rockwell sur tube en acier inoxydable est le même que le test de dureté Brinell.La différence est qu’il mesure la profondeur de l’indentation.Le test de dureté Rockwell est une méthode largement utilisée dans laquelle le HRC est utilisé juste après la dureté Brinell HB dans les normes sur les tuyaux en acier.La dureté Rockwell peut être appliquée à la détermination de matériaux métalliques extrêmement mous à très durs.Cela compense la méthode Brinell.Elle est plus simple que la méthode Brinell et permet de lire directement la valeur de dureté sur le cadran de la machine de dureté.Cependant, en raison de sa petite indentation, la valeur de dureté n'est pas aussi précise que la méthode Brinell.
Dureté Vickers
Le test de dureté Vickers sur tube en acier inoxydable est également une méthode de test d'indentation pour mesurer les matériaux métalliques très fins et la dureté de la couche superficielle.Elle présente les principaux avantages des méthodes Brinell et Rockwell et surmonte leurs inconvénients fondamentaux, mais elle n'est pas aussi simple que la méthode Rockwell.La méthode Vickers est rarement utilisée dans les normes sur les tuyaux en acier.
Test de duretée
Le tube en acier inoxydable a un diamètre intérieur de 6,0 mm ou plus et un tube en acier inoxydable recuit ayant une épaisseur de paroi de 13 mm ou moins.Il peut s'agir d'un testeur de dureté Vickers de type W-B75.Il est très simple et rapide à tester et convient à l’inspection rapide et non destructive des tuyaux en acier inoxydable.Les tubes en acier inoxydable d'un diamètre intérieur supérieur à 30 mm et d'une épaisseur de paroi supérieure à 1,2 mm sont testés avec un testeur de dureté Rockwell pour tester la dureté HRB et HRC.Les tubes en acier inoxydable d'un diamètre intérieur supérieur à 30 mm et d'une épaisseur de paroi inférieure à 1,2 mm sont testés avec un testeur de dureté de surface Rockwell pour tester la dureté HRT ou HRN.Pour les tuyaux en acier inoxydable d'un diamètre intérieur inférieur à 0 mm et supérieur à 4,8 mm, la dureté du HR15T est testée par un testeur de dureté Rockwell spécial pour tuyaux.Lorsque le diamètre intérieur du tube en acier inoxydable est supérieur à 26 mm, la dureté de la paroi intérieure du tube peut également être testée par un Ro
Composition chimique
| Notes | Cmax | Mn max | Pmax | Smax | Si max | Cr | Ni | Mo |
| 304 | 0,08 | 2h00 | 0,04 | 0,03 | 0,075 | 18h00-20h00 | 8h00-11h00 | / |
| 304L | 0,035 | 2h00 | 0,04 | 0,03 | 0,075 | 18h00-20h00 | 8h00-13h00 | / |
| 316 | 0,08 | 2h00 | 0,04 | 0,03 | 0,075 | 16h00-18h00 | 11h00-14h00 | 2h00-3h00 |
| 316L | 0,035 | 2h00 | 0,04 | 0,03 | 0,075 | 16h00-18h00 | 10h00-15h00 | 2h00-3h00 |
Propriétés mécaniques
| Notes | Article par article | Traction Psi | Rendement Psi | Allonger % | Dureté Rockwell |
| 304 | Recuit | 85000-105000 | 35000-75000 | 20-55 | 80-95 |
| 304L | Recuit I1/8 dur | 80000-105000 | 30000-75000 | 20-55 | 75-95 |
| 316 | Recuit | 85 000 minutes | 35 000 minutes | 50 minutes | 80 minutes |
| Recuit | 80 000 minutes | 30 000 minutes | 50 minutes | 75 minutes |
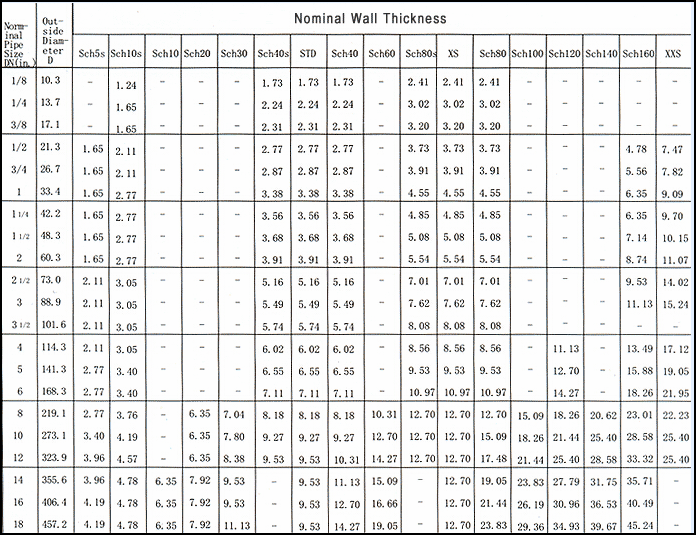
Tailles de tuyaux en acier inoxydable
Recuit et décapé, recuit brillant, poli
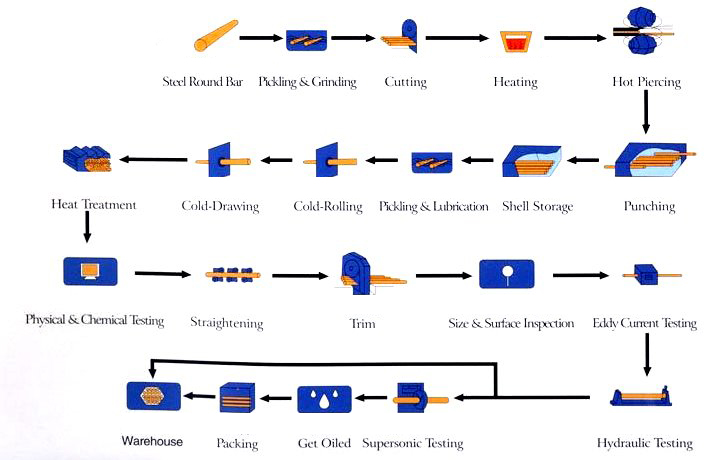
Processus