Elbow
Seamless Elbow Manufacturing Process (Heat Bending & Cold Bending)
One of the most common methods for manufacturing elbows is using hot mandrel bending from straight steel pipes. After heating the steel pipe at a elevated temperature, the pipe is pushed, expanded, bended by the inner tools of mandrel step by step. Applying hot mandrel bending can manufacture a wide size range seamless elbow. The characteristics of mandrel bending are strongely depend on the intergrated shape and dimensions of the mandrel. The using advantages of hot bending elbows include smaller thickness deviation and stronger bending radius than other bending methond type. Meanwhile, using bending instead of prefabricated bends substantially reduces the number of welds needed. This reduces the amount of work required and increases the quality and usability of pipes. However, cold bending is the process to bent the straight steel pipe at normal temperatures in a bending machine. Cold bending is suitable for pipes with an outer diameter of 17.0 to 219.1 mm, and wall thickness 2.0 to 28.0 mm. The recommended bending radius is 2.5 x Do. Normally at a bending radius of 40D. By using cold bending, we can get small radius elbows, but we need to pack the internals with sand to prevent wrinkling. Cold bending is a quick and inexpensive bending method. It is a competitive option for making pipelines and machine parts.
Welded Elbow Manufacturing Process (Small & Large)
Welded elbows are made from the steel plates, so it is not seamless steel elbows. Use a mould and press the steel plate to the shape of the elbow, then weld the seam to be a finish steel elbow. It is the old production method of the elbows. Recent years the small sizes elbows are almost manufactured from the steel pipes now. For the big size elbows, for example, it is very difficult to produce elbows over 36” OD from the steel pipes . So it is commonly made from the steel plates, pressing the plate to the shape of half elbow, and welding the two halves together. Since the elbows are welded in its body , the inspection of the welding joint is necessary . Commonly we use the X-Ray inspection as the NDT.
|
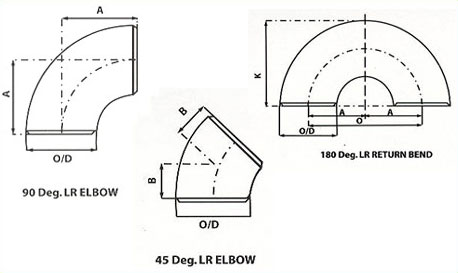
Nominal pipe size |
Outside Diameter |
Center to End |
Center to Center |
Back to Faces |
||||||
|
45°Elbows |
90°Elbows |
180°Return |
||||||||
|
H |
F |
P |
K |
|||||||
|
DN |
INCH |
Series A |
Series B |
LR |
LR |
SR |
LR |
SR |
LR |
SR |
|
15 |
1/2 |
21.3 |
18 |
16 |
38 |
- |
76 |
- |
48 |
- |
|
20 |
3/4 |
26.9 |
25 |
16 |
38 |
- |
76 |
- |
51 |
- |
|
25 |
1 |
33.7 |
32 |
16 |
38 |
25 |
76 |
51 |
56 |
41 |
|
32 |
11/4 |
42.4 |
38 |
20 |
48 |
32 |
95 |
64 |
70 |
52 |
|
40 |
11/2 |
48.3 |
45 |
24 |
57 |
38 |
114 |
76 |
83 |
62 |
|
50 |
2 |
60.3 |
57 |
32 |
76 |
51 |
152 |
102 |
106 |
81 |
|
65 |
21/2 |
76.1(73) |
76 |
40 |
95 |
64 |
191 |
127 |
132 |
100 |
|
80 |
3 |
88.9 |
89 |
47 |
114 |
76 |
229 |
152 |
159 |
121 |
|
90 |
31/2 |
101.6 |
- |
55 |
133 |
89 |
267 |
178 |
184 |
140 |
|
100 |
4 |
114.3 |
108 |
63 |
152 |
102 |
305 |
203 |
210 |
159 |
|
125 |
5 |
139.7 |
133 |
79 |
190 |
127 |
381 |
254 |
262 |
197 |
|
150 |
6 |
168.3 |
159 |
95 |
229 |
152 |
457 |
305 |
313 |
237 |
|
200 |
8 |
219.1 |
219 |
126 |
305 |
203 |
610 |
406 |
414 |
313 |
|
250 |
10 |
273.0 |
273 |
158 |
381 |
254 |
762 |
508 |
518 |
391 |
|
300 |
12 |
323.9 |
325 |
189 |
457 |
305 |
914 |
610 |
619 |
467 |
|
350 |
14 |
355.6 |
377 |
221 |
533 |
356 |
1067 |
711 |
711 |
533 |
|
400 |
16 |
406.4 |
426 |
253 |
610 |
406 |
1219 |
813 |
813 |
610 |
|
450 |
18 |
457.2 |
478 |
284 |
686 |
457 |
1372 |
914 |
914 |
686 |
|
500 |
20 |
508.0 |
529 |
316 |
762 |
508 |
1524 |
1016 |
1016 |
762 |
|
550 |
22 |
559 |
- |
347 |
838 |
559 |
Note: |
|||
|
600 |
24 |
610 |
630 |
379 |
914 |
610 |
||||
|
650 |
26 |
660 |
- |
410 |
991 |
660 |
||||
|
700 |
28 |
711 |
720 |
442 |
1067 |
711 |
||||
|
750 |
30 |
762 |
- |
473 |
1143 |
762 |
||||
|
800 |
32 |
813 |
820 |
505 |
1219 |
813 |
||||
|
850 |
34 |
864 |
- |
537 |
1295 |
864 |
||||
|
900 |
36 |
914 |
920 |
568 |
1372 |
914 |
||||
|
950 |
38 |
965 |
- |
600 |
1448 |
965 |
||||
|
1000 |
40 |
1016 |
1020 |
631 |
1524 |
1016 |
||||
|
1050 |
42 |
1067 |
- |
663 |
1600 |
1067 |
||||
|
1100 |
44 |
1118 |
1120 |
694 |
1676 |
1118 |
||||
|
1150 |
46 |
1168 |
- |
726 |
1753 |
1168 |
||||
|
1200 |
48 |
1220 |
1220 |
758 |
1829 |
1219 |
||||
ASTM A234
This specification covers wrought carbon steel & alloy steel fittings of seamless and welded construction. Unless seamless or welded construction is specified in order, either may be furnished at the option of the supplier. All welded construction fittings as per this standard are supplied with 100% radiography. Under ASTM A234, several grades are available depending upon chemical composition. Selection would depend upon pipe material connected to these fittings.
|
Tensile Requirements |
WPB |
WPC, WP11CL2 |
WP11CL1 |
WP11CL3 |
| Tensile Strength, min, ksi[MPa] | 60-85 | 70-95 | 60-85 | 75-100 |
| (0.2% offset or 0.5% extension-under-load) | [415-585] | [485-655] | [415-585] | [520-690] |
| Yield Strength, min, ksi[MPa] | 32 | 40 | 30 | 45 |
| [240] | [275] | [205] | [310] |
Some of the grades available under this specification and corresponding connected pipe material specification are listed below:
ASTM A403
This specification covers two general classes, WP & CR, of wrought austenitic stainless steel fittings of seamless and welded construction.
Class WP fittings are manufactured to the requirements of ASME B16.9 & ASME B16.28 and are subdivided into three subclasses as follows:
- WP – SManufactured from seamless product by a seamless method of manufacture.
- WP – W These fittings contain welds and all welds made by the fitting manufacturer including starting pipe weld if the pipe was welded with the addition of filler material are radiographed. However no radiography is done for the starting pipe weld if the pipe was welded without the addition of filler material.
- WP-WX These fittings contain welds and all welds whether made by the fitting manufacturer or by the starting material manufacturer are radiographed.
Class CR fittings are manufactured to the requirements of MSS-SP-43 and do not require non-destructive examination.
Under ASTM A403 several grades are available depending upon chemical composition. Selection would depend upon pipe material connected to these fittings. Some of the grades available under this specification and corresponding connected pipe material specification are listed below:
ASTM A420
This specification covers wrought carbon steel and alloy steel fittings of seamless & welded construction intended for use at low temperatures. It covers four grades WPL6, WPL9, WPL3 & WPL8 depending upon chemical composition. Fittings WPL6 are impact tested at temp – 50° C, WPL9 at -75° C, WPL3 at -100° C and WPL8 at -195° C temperature.
The allowable pressure ratings for fittings may be calculated as for straight seamless pipe in accordance with the rules established in the applicable section of ASME B31.3.
The pipe wall thickness and material type shall be that with which the fittings have been ordered to be used, their identity on the fittings is in lieu of pressure rating markings.
|
Steel No. |
Type |
Chemical composition |
||||||||||||
|
C |
Si |
S |
P |
Mn |
Cr |
Ni |
Mo |
Other |
ób |
ós |
δ5 |
HB |
||
| WPL6 | 0.3 | 0.15-0.3 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.6-1.35 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.12 | Cb:0.02;V:0.08 | 415-585 | 240 | 22 | ||
| WPL9 | 0.2 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.4-1.06 | 1.6-2.24 | 435-610 | 315 | 20 | ||||||
| WPL3 | 0.2 | 0.13-0.37 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.31-0.64 | 3.2-3.8 | 450-620 | 240 | 22 | |||||
| WPL8 | 0.13 | 0.13-0.37 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.9 | 8.4-9.6 | 690-865 | 515 | 16 | |||||
Light Oiling, Black Painting, Galvanizing, PE /3PE Anti-corrosion Coating
Packed in Wood Cabins/Wood Tray